
Code_Aster
®
Version
5.0
Titrate:
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
Date:
23/09/02
Author (S):
J.M. PROIX, F. LEBOUVIER
Key
:
V3.03.504-B
Page:
1/6
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
HT-66/02/001/A
Organization (S):
EDF/AMA, DeltaCAD
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
Document: V3.03.504
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up
of 3 layers, subjected to a loading
doubly sinusoidal
Summary:
This test represents the quasi-static calculation of a composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
supported, subjected to a doubly sinusoidal loading. This case-test makes it possible to validate modeling
finite elements DST with meshs TRIA3 and QUAD4, a composite material multi-layer.
Displacements and the stresses obtained are compared with a numerical reference solution.
Code_Aster
®
Version
5.0
Titrate:
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
Date:
23/09/02
Author (S):
J.M. PROIX, F. LEBOUVIER
Key
:
V3.03.504-B
Page:
2/6
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
HT-66/02/001/A
1
Problem of reference
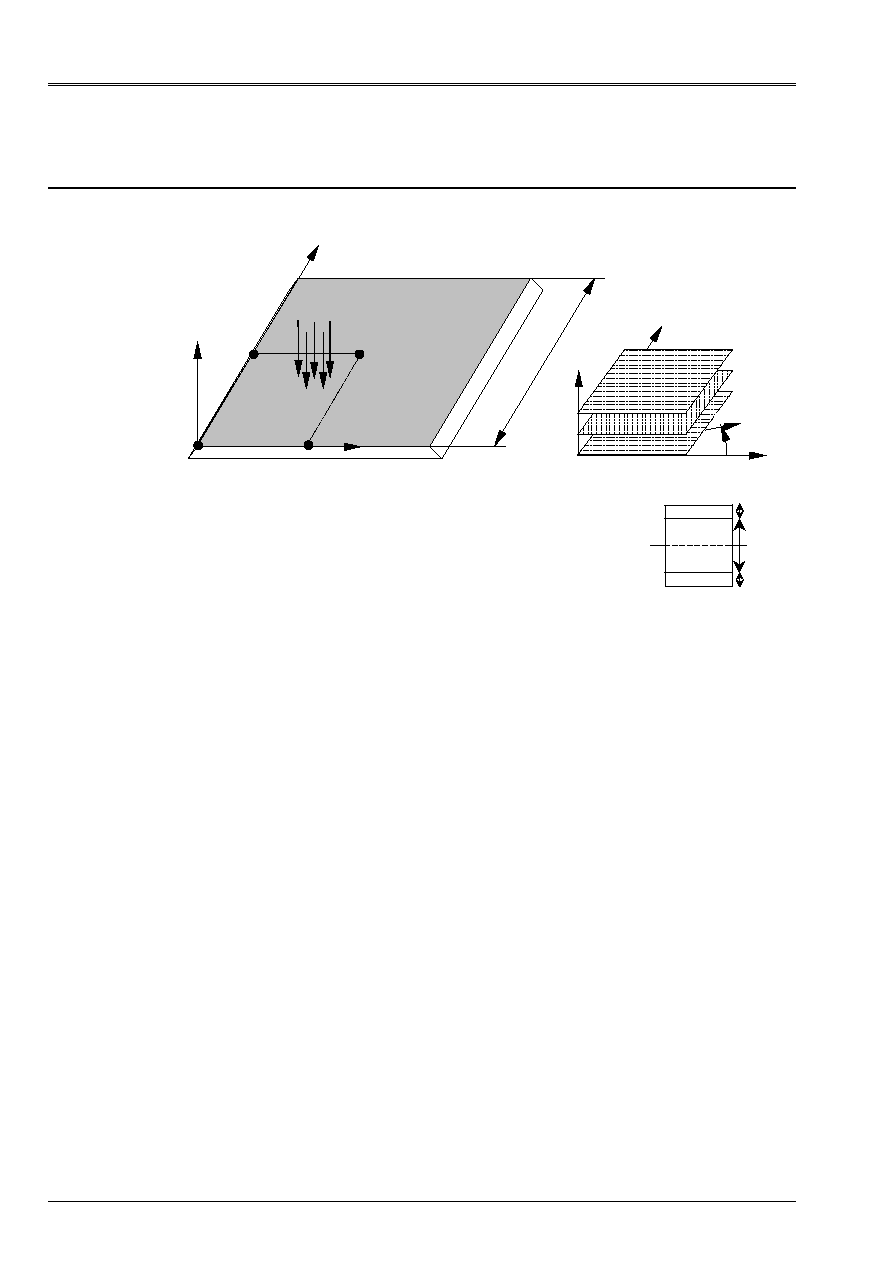
1.1 Geometry
L
X, U
Z, W
y, v
L = 1. m
H = 0.1 m
D
B
C
0°
90°
0°
Stacking
p=p
O
sin (
X/L
)
sin (
y/L
)
With
L
Z
T
H/4
H/2
H/4
The 3 layers have as a relative thickness: H/4, H/2, H/4
1.2
Properties of material
The axes of orthotropism correspond to the curvilinear directions X and Y.
E
L
= 25.
E
T
= 1. (L X; T y)
G
G
lt
lz
=
= 0.5
G
tz
= 0.2
lt
= 0.25
1.3
Boundary conditions and loadings
·
CL: displacement perpendicular to the plate, to its contour is null.
·
Loading: p = p
O
sin (
X/L
)
sin (
y/L
)
with p
O
=0.01
1.4 Conditions
initial
Without object

Code_Aster
®
Version
5.0
Titrate:
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
Date:
23/09/02
Author (S):
J.M. PROIX, F. LEBOUVIER
Key
:
V3.03.504-B
Page:
3/6
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
HT-66/02/001/A
2
Reference solution
2.1
Method of calculation used for the reference solution
The reference solution is a numerical solution [bib3].
2.2
Results of reference
The numerical results of reference are as follows:
Size
DST *
(TRIA3)
DST * (QUAD4)
·
Displacement W at the point C (L/2, L/2,0)
0.07323 0.07417
·
Stress
xx
at the point C (L/2, L/2, H/2) (layer 3)
0.478 0.482
·
Stress
yy
at the point C (L/2, L/2, H/4) (layer 2)
0.339 0.4
·
Stress
xz
at the point D (0, L/2,0) (layer 2)
0.0203 0.0305
·
Stress
yz
at the point B (L/2,0,0) (layer 2)
0.0406 0.0204
* the reference solutions were obtained with a mesh 6x6 [bib3].
2.3
Uncertainties on the solution
< 2%
2.4 References
bibliographical
[1]
BATOZ J.L., DHATT G.: Modeling of the structures by finite elements, Flight 2, Beams and
Plates, HERMES.
[2]
PAGANO N.J., Hatfield J.J. : “Elastic behavior off multilayered bidirectional composite”,
AIAA J., Flight 10, N°7, p. 931-933, 1972.
[3]
LARDEUR P.: Development and evaluation of two new finite elements of plates and
composite hulls with influence of transverse shearing, Thesis of Doctorate
Engineer, University of Technology of Compiegne, 1990.
Code_Aster
®
Version
5.0
Titrate:
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
Date:
23/09/02
Author (S):
J.M. PROIX, F. LEBOUVIER
Key
:
V3.03.504-B
Page:
4/6
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
HT-66/02/001/A
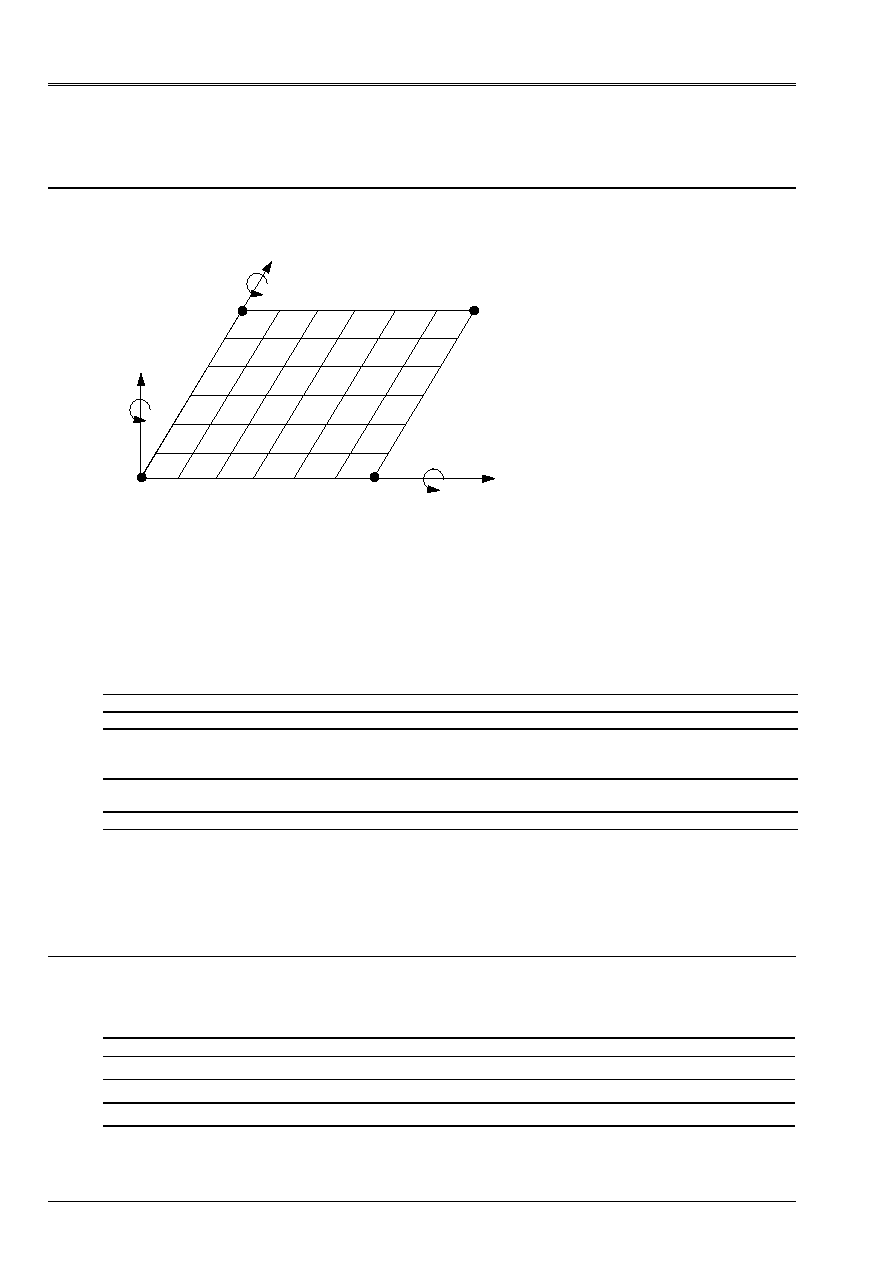
3 Modeling
With
3.1
Characteristics of modeling
X, U
Z, W
y, v
D
B
C
With
Z
X
y
Modeling DST (QUAD4)
- Boundary conditions:
. Dimensioned AB: W =
y
=0
. Dimensioned AD: W =
X
=0
- Conditions of symmetry:
. Dimensioned BC: U =
y
= 0
. Dimensioned CD: v =
X
= 0
3.2
Characteristics of the mesh
A number of nodes: 49
A number of meshs and type: 36 QUAD4
3.3 Functionalities
tested
Controls Key word
factor
Key word
AFFE_MODELE
AFFE
“DST”
DEFI_MATERIAU
ELAS_ORTH
DEFI_COQU_MULT
SLEEP
THICK
MATER
ORIENTATION
AFFE_CARA_ELEM
HULL
THICK
ANGL_REP
AFFE_CHAR_MECA_F
FORCE_COQUE
NEAR
CALC_CHAM_ELEM
NUME_COUCHE
NIVE_COUCHE
OPTION
“SUP” “MOY”
“SIGM_ELNO_DEPL”
4
Results of modeling A
4.1 Values
tested
Identification Reference
Aster Difference
(%)
Displacement W at the point C (L/2, L/2,0)
0.07417 0.07444
0.37
Stress
xx
at the point C (L/2, L/2, H/2)
0.482 0.474
1.7
Stress
yy
at the point C (L/2, L/2, H/4)
0.400 0.412
3
Stress
xz
at the point D (0, L/2,0)
0.0305 0.03
1.7
Stress
yz
at the point B (L/2,0,0)
0.0204 0.021
2.8
Code_Aster
®
Version
5.0
Titrate:
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
Date:
23/09/02
Author (S):
J.M. PROIX, F. LEBOUVIER
Key
:
V3.03.504-B
Page:
5/6
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
HT-66/02/001/A
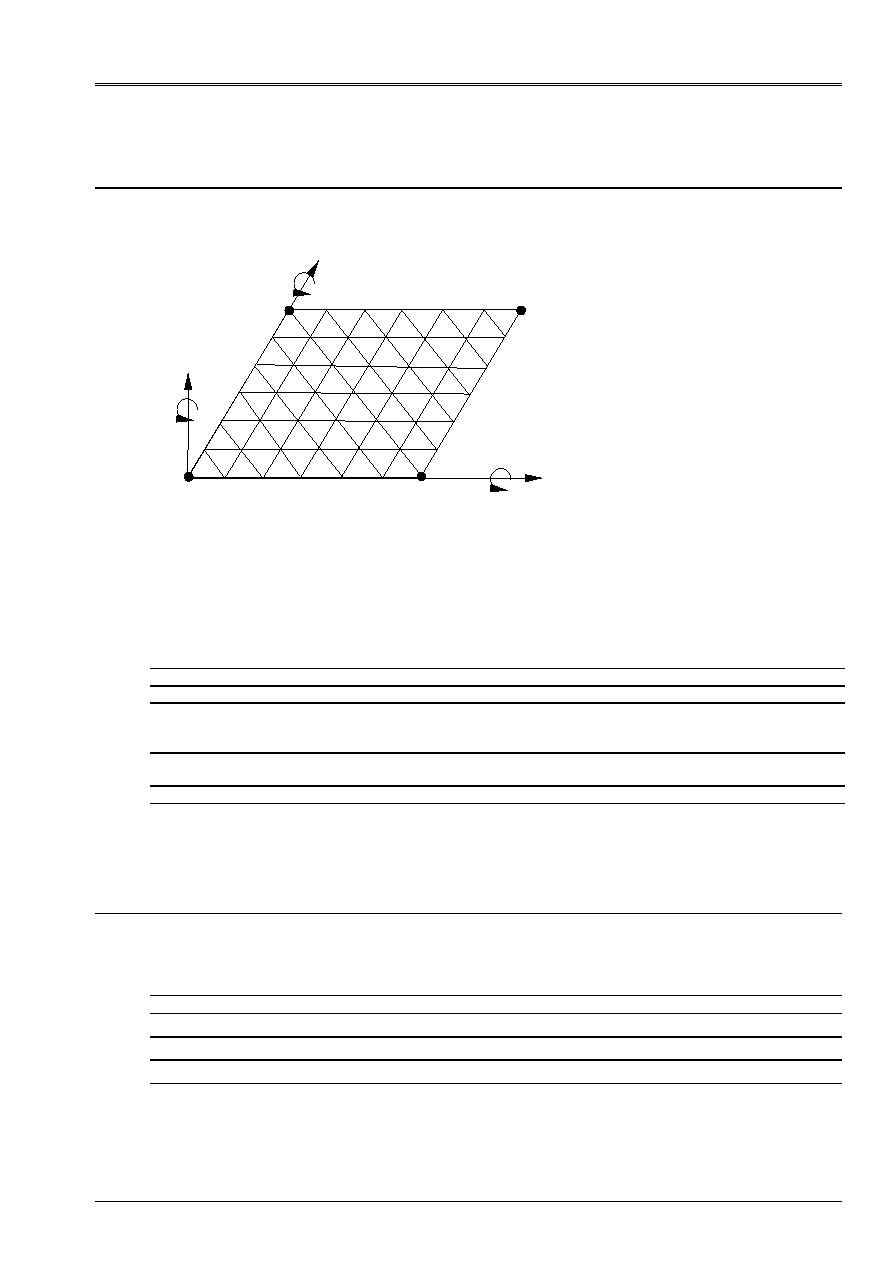
5 Modeling
B
5.1
Characteristics of modeling
X, U
Z, W
y, v
D
B
C
With
Z
X
y
Modeling DST (TRIA3)
- Boundary conditions:
. Side AB: W =
y
=0
. Side AD: W =
X
=0
- Conditions of symmetry:
. Side BC: U =
y
= 0
. Side CD: v =
X
= 0
5.2
Characteristics of the mesh
A number of nodes: 49
A number of meshs and type: 72 TRIA3
5.3 Functionalities
tested
Controls Key word
factor
Key word
AFFE_MODELE
AFFE
“DST”
DEFI_MATERIAU
ELAS_ORTH
DEFI_COQU_MULT
SLEEP
THICK
MATER
ORIENTATION
AFFE_CARA_ELEM
HULL
THICK
ANGL_REP
AFFE_CHAR_MECA_F
FORCE_COQUE
NEAR
CALC_CHAM_ELEM
NUME_COUCHE
NIVE_COUCHE
OPTION
“SUP” “MOY”
“SIGM_ELNO_DEPL”
6
Results of modeling B
6.1 Values
tested
Identification Reference
Aster Difference
(%)
Displacement W at the point C (L/2, L/2,0)
0.07323 0.07112
2.9
Stress
xx
at the point C (L/2, L/2, H/2)
0.478 0.4621 3.3
Stress
yy
at the point C (L/2, L/2, H/4)
0.339 0.3413
0.7
Stress
xz
at the point D (0, L/2,0)
0.0203 0.0217
7.3
Stress
yz
at the point B (L/2,0,0)
0.0406 0.0435
7.3

Code_Aster
®
Version
5.0
Titrate:
SSLS504 - Composite square plate made up of 3 layers, simply
Date:
23/09/02
Author (S):
J.M. PROIX, F. LEBOUVIER
Key
:
V3.03.504-B
Page:
6/6
Manual of Validation
V3.03 booklet: Linear statics of the plates and hulls
HT-66/02/001/A
7
Summary of the results
·
Displacements: the result obtained with meshs QUAD4 is satisfactory (variation of 0.4%). One
observe a more important variation (3%) for meshs TRIA3.
·
Stresses: the result obtained with meshs QUAD4 is satisfactory (maximum change of 3%).
One observes a more important variation (7%) for meshs TRIA3.
This test thus makes it possible to validate the calculation of the composite plates under loading function of
geometry, as well in term of displacements of stresses.





