|
Pressure, density and temperature of a gas are related through an
equation of state. Under ordinary conditions for air,
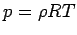 |
(1.17) |
where p is the absolute pressure, 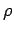 the density, T the
absolute temperature and R is a gas constant. The above equation
is called the Ideal Gas Law or the Perfect Gas
Equation. The gases obeying this equation are called
Ideal Gases. the density, T the
absolute temperature and R is a gas constant. The above equation
is called the Ideal Gas Law or the Perfect Gas
Equation. The gases obeying this equation are called
Ideal Gases.
The gas constant R (Ideal Gas Law ) is given by
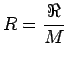 |
(1.18) |
where 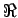 is called the universal gas constant and is equal to
8314 J/kg.K. For air the gas constant R = 286.9 J/kg.K . is called the universal gas constant and is equal to
8314 J/kg.K. For air the gas constant R = 286.9 J/kg.K .
(c) Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic Engg. 2005
University of Sydney
|

