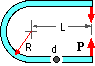
 A spring is formed by bending a rod of diameter d into a U-shape of radius R and leg length L, where R, L >> d.
A spring is formed by bending a rod of diameter d into a U-shape of radius R and leg length L, where R, L >> d.
Show that the spring's compliance (reciprocal stiffness) is 32( 4L3 +6πRL2 +24R2 L +3πR3 )/ 3πEd4
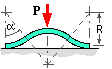 A spring is made by curving a strip of rectangular cross-section into four identical arcs of radius R and included angle α, as shown. Neglecting friction, show that the deflection, δ, experienced by the load P is :- δ = ( PR3 /4EI )[ 3( 2α +sin2α ) - 4α cos2α - 8 sinα ]
A spring is made by curving a strip of rectangular cross-section into four identical arcs of radius R and included angle α, as shown. Neglecting friction, show that the deflection, δ, experienced by the load P is :- δ = ( PR3 /4EI )[ 3( 2α +sin2α ) - 4α cos2α - 8 sinα ]
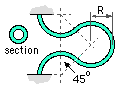 The flexible pipe loop may be placed between a steam boiler and process plant to reduce the forces caused by thermal expansion of the pipe. Determine the force and moment developed by a temperature rise of T over that at installation. Hint: allow the pipe to expand freely then load it to negate the expansion.
The flexible pipe loop may be placed between a steam boiler and process plant to reduce the forces caused by thermal expansion of the pipe. Determine the force and moment developed by a temperature rise of T over that at installation. Hint: allow the pipe to expand freely then load it to negate the expansion.
[ 0.228 EI αT/R2 ]
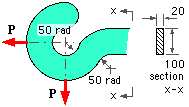 A hook, of uniform rectangular cross-section and made from a steel whose design stress is 100 MPa, may support a load, P, in either of the two positions shown. What maximum load can the hook sustain ?
A hook, of uniform rectangular cross-section and made from a steel whose design stress is 100 MPa, may support a load, P, in either of the two positions shown. What maximum load can the hook sustain ? [ 12.6 kN ]
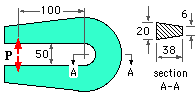
[ 119 MPa (t), 83 MPa (c) ]
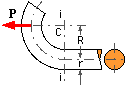 The end of a straight round rod of radius r is bent to a circular arc of
mean radius R. The severity of curvature is characterised by the ratio λ = r/R.
The end of a straight round rod of radius r is bent to a circular arc of
mean radius R. The severity of curvature is characterised by the ratio λ = r/R.
The rod supports a force P which acts through the centre of curvature C, normal to the interface i-i between straight and curved portions.
If σd = P/A is the direct stress, show that the maximum stress is
σd. [λ/(1-λ)] [ 1 +√(1-λ2 )] / [ 1 -√(1-λ2 )] in a cross-section just to the left of i-i, and
σd. ( 1 + 4 / λ ) in a cross-section just to the right of i-i as sketched.
Plot these expressions versus λ ( 0≤λ≤1 ), comment on the trends displayed, and evaluate the curvature-induced stress concentration for λ = 0.05, 0.5, 0.95.
[ 1.04, 1.55, 6.96 ]
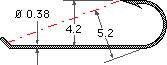 A fish hook is forged from wire having a yield strength of 2.3 GPa. Assuming a straight pull from the leader through the point, estimate the load which would cause the hook to yield.
A fish hook is forged from wire having a yield strength of 2.3 GPa. Assuming a straight pull from the leader through the point, estimate the load which would cause the hook to yield. [ 2.2 N ]
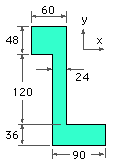
[ 1.52 ]
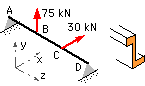 The beam ABCD, simply supported at A and D and otherwise identical to that above, is loaded by 75 kN at B, in line with the web, and by 30 kN at C parallel to the flanges (AB=BC=CD=1 m). Determine the safety factor.
The beam ABCD, simply supported at A and D and otherwise identical to that above, is loaded by 75 kN at B, in line with the web, and by 30 kN at C parallel to the flanges (AB=BC=CD=1 m). Determine the safety factor.
[1.12]
 Properties of materials used in the joint are :
Properties of materials used in the joint are :
| steel | bronze | cast iron | ||
| elastic modulus ( GPa ) | 207 | 110 | 100 | |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.21 | |
| design stress ( MPa ) | 400 | 240 | 100(t), 350(c) |
- the socket material is bronze and failure occurs due to lubrication breakdown occasioned by the contact pressure exceeding 200 MPa. [ 1.70 kN ]
- failure is due to material strength limitations. [ 13.6 kN ]
- as (b), but the socket material is cast iron. [ 11.0 kN ]
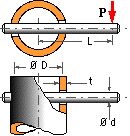 A wrench, required to produce a torque of 300 Nm, is made from a tube of 50 mm mean diameter and wall thickness t, through which two diametrically opposite holes are drilled. A detachable solid handle, of nominal diameter d, fits through these holes with a diametral clearance of 1%. The torque is generated by a force applied at some distance along the handle. Both components are of steel with design (tensile) stresses of 200 and 300MPa for tube and handle respectively.
A wrench, required to produce a torque of 300 Nm, is made from a tube of 50 mm mean diameter and wall thickness t, through which two diametrically opposite holes are drilled. A detachable solid handle, of nominal diameter d, fits through these holes with a diametral clearance of 1%. The torque is generated by a force applied at some distance along the handle. Both components are of steel with design (tensile) stresses of 200 and 300MPa for tube and handle respectively.
Suggest suitable dimensions for the wrench.
Indicate the effect on the selected dimensions if the diametral clearance is changed to 5%, to facilitate handle engagement.