[ 353, 310, 193 mm]
( b) If the pitch length of the above belt is 3080 mm, what then is the rating and what is the corresponding power correction factor for pitch length? Check this last value with the Code. [ 3.50 kW, 1.14]
( c) If the drive in ( a) is required to last for only 10 kh, by what percentage is the above capacity increased? [ 24%]
( a) What is the capacity of this drive using the Code method ? [ 6.04 kW]
( b) What is the life of the drive when transmitting 6.04 kW ? [ 31 kh]
( c) Repeat ( a), but use ( 5a) with the standard life of 26 kh. [ 6.19 kW]
( d) Check this last result using the program V-belts.
( e) A multi-strand drive, otherwise identical to the above, is required to transmit 12 kW with a duty factor of 1.3. Use ( 5a) to determine the number of belts required. [ 2.5]
( f) What life may be expected, if 2, or if 3 belts are used ? [ 5.0, 82 kh]
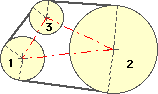 into the drive whose layout is sketched. The wrap angle on the 150 mm diameter motor pulley (1) is 118o and the pulley rotates at 2880 rpm. The 400 mm diameter driven pulley (2) absorbs the design power of 10 kW. Pulley (3), of 80 mm diameter, is an idler and absorbs no appreciable power.
into the drive whose layout is sketched. The wrap angle on the 150 mm diameter motor pulley (1) is 118o and the pulley rotates at 2880 rpm. The 400 mm diameter driven pulley (2) absorbs the design power of 10 kW. Pulley (3), of 80 mm diameter, is an idler and absorbs no appreciable power.
Estimate the life of the belts if . . . . .
( a) the pulleys rotate clockwise, or
( b) they rotate counterclockwise, or
( c) the idler is removed and the centre distance between (1) and (2) increased accordingly. [ 6, 0.6, 14 kh ]
Select a drive for this duty.
Select a squirrel cage motor and finalise the drive, including pivot location.
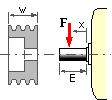 A squirrel cage motor is usually equipped with deep groove ball bearings, but life considerations might require replacement of the drive-end bearing by a larger capacity roller bearing when :
A squirrel cage motor is usually equipped with deep groove ball bearings, but life considerations might require replacement of the drive-end bearing by a larger capacity roller bearing when :
- the shaft load is heavy due to a small belt pulley for example, or
- the load overhang ('x' in the diagram) is large.
An ABB motor t
| life (kh) | 40 | 63 |
| F0 at x=0 (kN) | 7.32 | 6.29 |
| FE at x=E (kN) | 6.18 | 5.31 |
Will the drive-end ball bearing last for the target life of 25 kh or is a roller bearing needed?
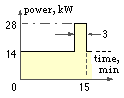 This concerns part-load belt tensions and components with different load-life equations.
This concerns part-load belt tensions and components with different load-life equations.
Select a squirrel cage motor and fixed centre belts to drive an agitator at about 700 rpm for 1 kh per annum. The power demand varies cyclically as shown and a 3-year belt replacement period is acceptable.
The drive should be compact, but not to the extent that the motor's usual ball bearings have to be replaced by roller bearings.
For the purposes of this problem, motors' maximum shaft loads tabulated in the Motors chapter refer to loads at the end of the shaft (FE of the previous problem), to bearing lives of 40 kh, and to a load-life index of n = 2.5.