



: begin a new document.
: open a new document.
: close your document.
: this is used when working with multiple files. Having a master document will let you work more easily with other .tex files included in your document.
: compiles your LATEX source code and displays the results automatically, unless you have code errors.
: this mode will "watch" the DVI file for changes, and will not launch a new session of KDVI after .
: views the .log file, so you can spot errors.
: jumps backward through the .log file and highlights errors in source.
: jumps forward through .log file and highlights errors in source.
: halts current function.
: runs LATEX on the active document.
: launches DVI viewer.
: converts DVI file to a PostScript (PS).
: launches PostScript (PS) viewer.
: creates PDF from LATEX source, if you have a LATEX header.
: views PDF.
: converts a DVI to a PDF.
: converts a PS to a PDF.
: creates HTML code from LATEX source.
: views HTML created.
: jump to page that corresponds to the current line in the editor.
If you look at the Edit toolbar, you will notice three large drop-down menus. The drop-down menus were designed for you to be able to quickly add certain common features into your document. The first drop-down box is used for quickly dividing your document by parts, chapter, sections and so on; the available commands to add segments to your LATEX source code are:
part: highest level of sectioning for a document.
chapter: starts a new chapter.
section: create a new section.
subsection: create a new subsection.
subsubsection: a secondary section between subsection and paragraph.
paragraph: create a new paragraph.
subparagraph: create a new subparagraph.
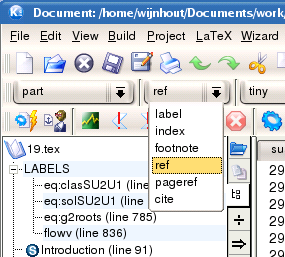
The drop-down box named label is used to insert items to your document such as indexes, footnotes, and references; the available commands are:
label: a command that produces a label for a chapter, a figure or another element.
index: creates an entry for the index.
footnote: creates a footnote in your document.
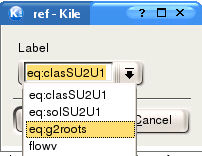
ref: used to refer to a predefined label, which you can choose from a drop-down list.
pageref: just like ref, but refers to a page instead of a structure element.
cite: create a reference with data from a bibliography.
When using cite, you are presented with a drop-down list of bibitems, but if you are using BibTEX this will only work if the file belongs to a Project. You can also use gBib or pyBliographer, or do it by hand.
The last drop-down box labeled tiny is used to set the size of the text. You can set the size of the main text, of footnotes, and so on. The available commands are:
tiny: smallest.
scriptsize: very small.
footnotesize: smaller.
small: small.
normalsize: normal.
large: large.
Large: larger.
LARGE: even larger.
huge: still larger.
Huge: largest.