Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
1/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
Organization (S):
EDF-R & D/AMA
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
Document: R4.01.02
Anisotropic elasticity
Summary
This document treats anisotropic elasticity.

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
2/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
Count
matters

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
3/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
1 Introduction
The objective of this document is to give the form of the matrices of flexibility and Hooke for
elastic materials orthotropic, isotropic transverse and isotropic in the cases 3Dn 2D-stresses,
plane 2D-deformations and axisymetry.
We speak about “matrices” of Hooke because, by preoccupation with a simplification, we did not adopt
notation of a tensor of command 4.
In any rigor, for linear elastic materials, the stresses are linear functions
deformations.
One writes:
ij = Hijkl. kl
The symmetrical nature of [
] and [] and adoption for these tensors of command 2d' a vectorial form
allows to write:
{}
[]
{}
H
=
or
{}
and
{}
are the vectorial representation of the tensors of command 2
{}
and
[]
and where [H] is one
stamp 6 X 6.
2
Topology of the matrices of Hooke
2.1 Orthotropism
One can show the symmetry of the matrix of Hooke H.
We thus have twenty and one independent components in the case 3D.
[]
66
56
55
46
45
44
36
35
34
33
26
25
24
23
22
16
15
14
13
12
11
H
H
H
H
H
H
SYM
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
=
An orthotropic material has two orthogonal plans of elastic symmetry.
This wants to say that if one calls [H'] the matrix [H] after symmetry (S)
[H'] = [H].
The relations obtained between the coefficients make it possible to write that [H] is defined by new
independent components.
Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
4/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
In the axes of orthotropism:
[]
66
55
44
33
23
22
13
12
11
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
H
H
H
SYM
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
=
9 coefficients thus should be provided.
2.2 Isotropy
transverse
The transverse isotropy is a restriction of the orthotropism in where one has the isotropy in one of both
orthogonal plans of elastic symmetry.
The matrix [H] will have the same form as for the orthotropism but with additional relations
between the components.
5 components are enough to determine [H].
2.3 Isotropy
The material is isotropic if [H] remains invariant in any change of reference mark.
Two coefficients are enough to determine [
H].
3
Stamp of Hooke and flexibility
3.1 Notations
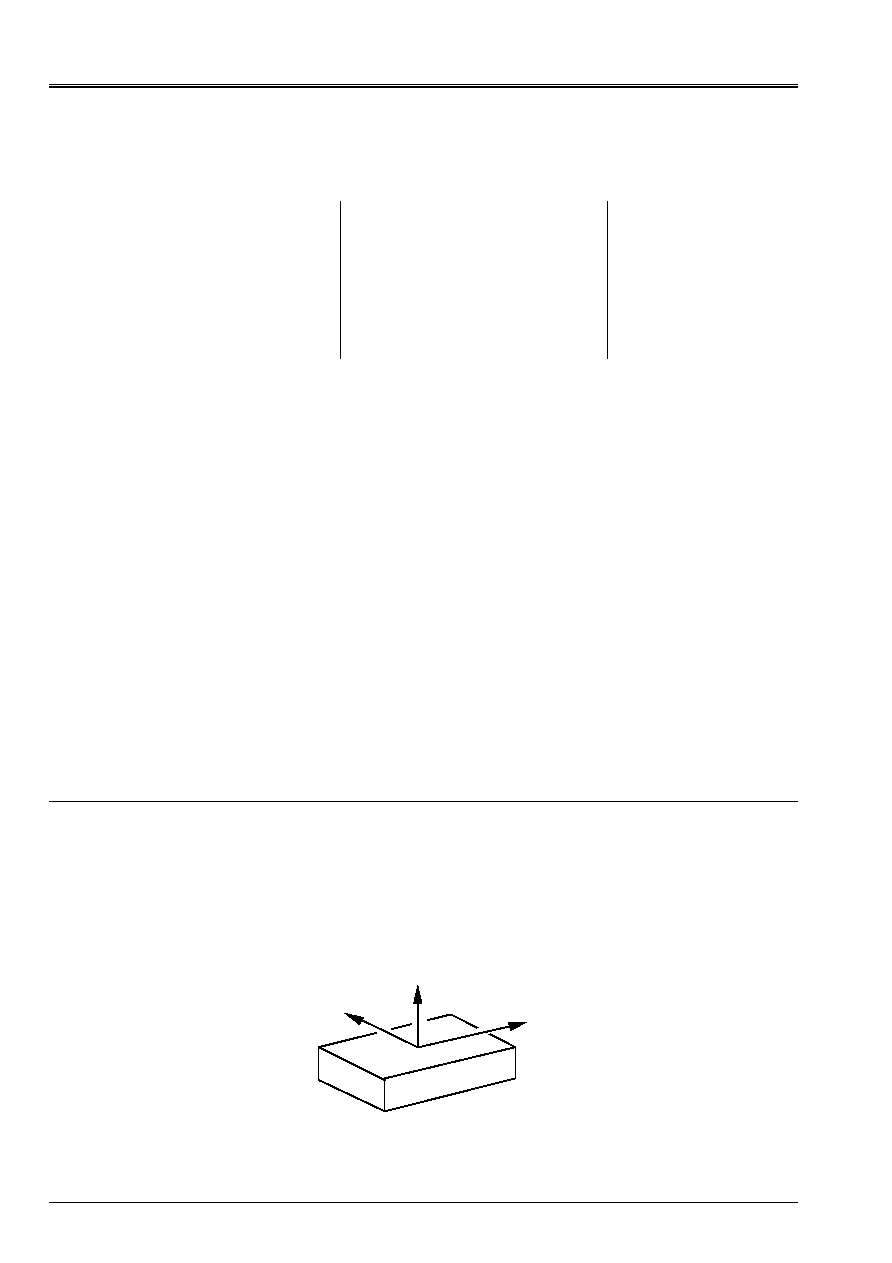
Instead of using indices 1, 2 and 3 to identify the axes, one will use the corresponding indices L,
T and NR:
L for longitudinal
T for transverse
NR for normal
NR
T
L
Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
5/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
The coefficients which intervene are as follows:
E_L
: Longitudinal Young modulus
E_T
: Transverse Young modulus
E_N
: Normal Young modulus
G_LT
: Modulus of rigidity in the plan (L, T)
G_TN
: Modulus of rigidity in the plan (T, NR)
G_LN
: Modulus of rigidity in the plan (L, NR)
NU_LT: Poisson's ratio dasn the plan (L, T)
NU_TN: Poisson's ratio in the plan (T, NR)
NU_LN: Poisson's ratio in the plan (L, NR)
Very important remark:
LT
Naked _
is different from
TL
Naked _
:
If one applies a traction according to L
L
L
L
E
=
(law of Hooke following a direction).
This traction is accompanied, proportionally, of a contraction according to
L
L
E
LT
Naked
T
.
_
,
-
and of a contraction according to
L
L
E
LN
Naked
NR
_
,
-
.
The first index indicates the axis where the effect of the loading is exerted and the second index indicates
direction of the loading.
Then one exerts a traction according to T, then a traction according to NR; one obtains:
()
S
E
E
NT
Naked
E
NL
Naked
E
TN
Naked
E
E
TL
Naked
E
LN
Naked
E
LT
Naked
E
NR
NR
T
TT
L
L
NR
NR
NR
T
TT
L
L
TT
NR
NR
T
TT
L
L
L
+
-
-
=
-
+
-
=
-
-
=
_
_
_
_
_
_
The matrix of flexibility [H]
1
is symmetrical; one deduces some:
T
L
E
TL
Naked
E
LT
U
_
_
=
NR
L
E
NL
Naked
E
LN
Naked
_
_
=
NR
T
E
NT
Naked
E
TN
Naked
_
_
=
In all that follows NAKED will be noted
.

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
6/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
3.2
Case 3D
3.2.1 0rthotropie
3.2.1.1 Stamp flexibility
-
-
-
-
-
-
=
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
T
NT
L
NL
NR
TN
T
L
TL
NR
LN
LT
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
G
G
SYM
G
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
H
1
Orthotropie
3.2.1.2 Stamp of Hooke
(
) (
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
) (
) (
)
-
+
+
+
-
+
+
+
-
=
-
-
-
-
=
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
T
L
TL
LT
T
L
NL
LT
NT
T
L
TL
NT
NL
NR
L
TL
LN
TN
NR
L
LN
NL
NR
L
NL
TN
TL
NR
T
TN
LT
LN
NR
T
NT
LN
LT
NR
T
NT
TN
LT
NL
TN
TL
LT
LN
NL
NT
TN
NR
T
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
L
L
GTN
GLN
SYM
GLT
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
*
0
*
0
0
*
0
0
0
.
.
1
.
.
.
.
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
0
0
0
.
.
1
1
2
1
H Orthotropie with
N
TN
T
NT
NR
LN
L
NL
T
LT
L
TL
E
E
E
E
E
E
=
=
=
;
;
Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
7/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
3.2.2 Isotropy
transverse
3.2.2.1 Stamp flexibility
NR
T
L
The H1 matrix can be deduced directly from the matrix H1-Orthotropism by using the properties
transverse isotropy.
In the plan (L, T):
(
)
LT
L
LT
TL
TL
T
L
E
G
E
E
+
=
=
=
1
2
In the plans (L, NR) and (T, NR):
LN
TN
TN
LN
NL
NT
G
G
=
=
=
Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
8/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
NR
T
L
(
)
NR
LN
L
NT
LN
TN
TN
LN
NL
NT
LT
L
LT
TL
LT
T
L
E
E
G
G
E
G
E
E
=
=
=
= +
=
=
=
1
2
(
)
+
-
-
-
-
-
-
=
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
TN
LN
L
LT
NR
L
NT
L
NL
NR
LN
L
L
TL
NR
LN
L
LT
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
G
G
SYM
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1
0
1
0
0
1
2
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
H1 - Isotropy transverse
Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
9/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
3.2.2.2 Stamp of Hooke
The matrix [H] has same symmetries as [H]
1
NR
T
L
(
)
+
-
+
+
+
-
+
+
+
-
=
-
-
-
=
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
LN
LN
LT
L
L
LT
L
NL
LT
NL
L
NL
LT
NL
NR
L
LN
LT
LN
NR
L
LN
NL
NR
L
LN
NL
TL
NR
L
LN
LT
LN
NR
L
LN
NL
LT
NR
L
LN
NL
LT
LN
NL
LT
LN
NL
NR
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
G
G
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
'
.
'
.
1
2
'
.
0
0
0
1
.
.
0
0
0
.
.
.
1
.
0
0
0
.
.
.
.
1
1
2
.
2
1
.
2
2
2
2
2
2
H transverse Isotropie

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
10/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
3.2.3 Isotropy
3.2.3.1 Stamp flexibility according to E and
(
)
(
)
+
=
+
=
+
=
-
-
-
=
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
E
G
E
G
SYM
E
G
E
E
E
E
E
E
1
2
1
0
1
2
1
0
0
)
1
(
2
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
H
1
Complete Isotropie
3.2.3.2 Stamp of Hooke according to E and
(
) (
)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
+
=
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
TN
LN
LT
NR
TT
L
SYM
E
2
2
1
0
2
2
1
0
0
2
2
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
2
1
1
H complete Isotropie

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
11/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
3.2.3.3 Stamp flexibility according to the coefficients of Lamé
and µ
The law of Hooke takes the following form with the coefficients of Lamé
and µ.
ij
ij
ij
kk
µ
2
+
=
By using the system of equations (S), one obtains:
-
=
LT
NR
TT
L
LT
T
L
LT
T
TL
L
TL
LT
LT
NR
TT
L
G
E
E
E
E
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
.
0
0
.
.
1
1
H Orthotropie planes in plane stresses
3.2.3.4 Stamp of Hooke according to the coefficients of Lamé
and µ
+
+
+
=
TN
LT
LN
NR
TT
L
TN
LT
LN
NR
TT
L
SYM
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
0
0
0
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
2
H Isotropie supplements with the coefficients of Lamé
3.3
Orthotropic in plane deformations and axisymmetric case 2D
3.3.1 Stamp flexibility
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
-
+
-
+
-
-
=
LT
NR
TT
L
LT
NT
TN
T
NT
LN
LT
T
NL
TN
TL
L
LN
NL
L
LT
TT
L
G
E
E
E
E
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
.
1
1
.
1
0
0
.
1
.
1
1
0
H-1 Orthotropie planes in plane deformations and axisymetry

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
12/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
3.3.2 Stamp of Hooke
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
+
+
+
+
+
-
-
+
+
+
+
+
-
=
LT
TT
L
LT
NL
LT
NT
NR
TL
NT
NL
NR
NL
LT
NT
T
LN
NL
T
NL
TN
TL
T
TL
NT
NL
NR
NT
LN
LT
NT
TN
L
LT
NR
TT
L
G
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
0
0
0
0
0
0
'
.
'
0
1
'
.
1
'
'
0
'
.
'
.
1
'
LT
NL
TN
TL
LT
LN
NL
NT
TN
2
.
.
.
1
'
-
-
-
-
=
H Orthotropie planes in plane deformations and axisymetry
3.4
Orthotropic case 2D in plane stresses
3.4.1 Stamp flexibility
-
-
=
LT
NR
TT
L
LT
T
L
TL
T
LT
L
LT
NR
TT
L
G
E
E
E
E
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
H
1
Orthotropie planes in plane stresses
3.4.2 Stamp of Hooke
-
=
LT
NR
TT
L
LT
T
L
LT
T
TL
L
TL
LT
LT
TT
L
G
E
E
E
E
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
.
1
1
0
H Orthotropie in plane stresses
Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
13/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
4 Use
in
Code_Aster
In Aster, the definition of the constant orthotropic elastic characteristics or functions of
temperature are carried out by the control DEFI_MATERIAU, key word ELAS_ORTH or ELAS_ORTH_FO
for the elements of hull and the solid elements isoparametric or the constitutive layers
of a composite (see control DEFI_COQU_MULT).
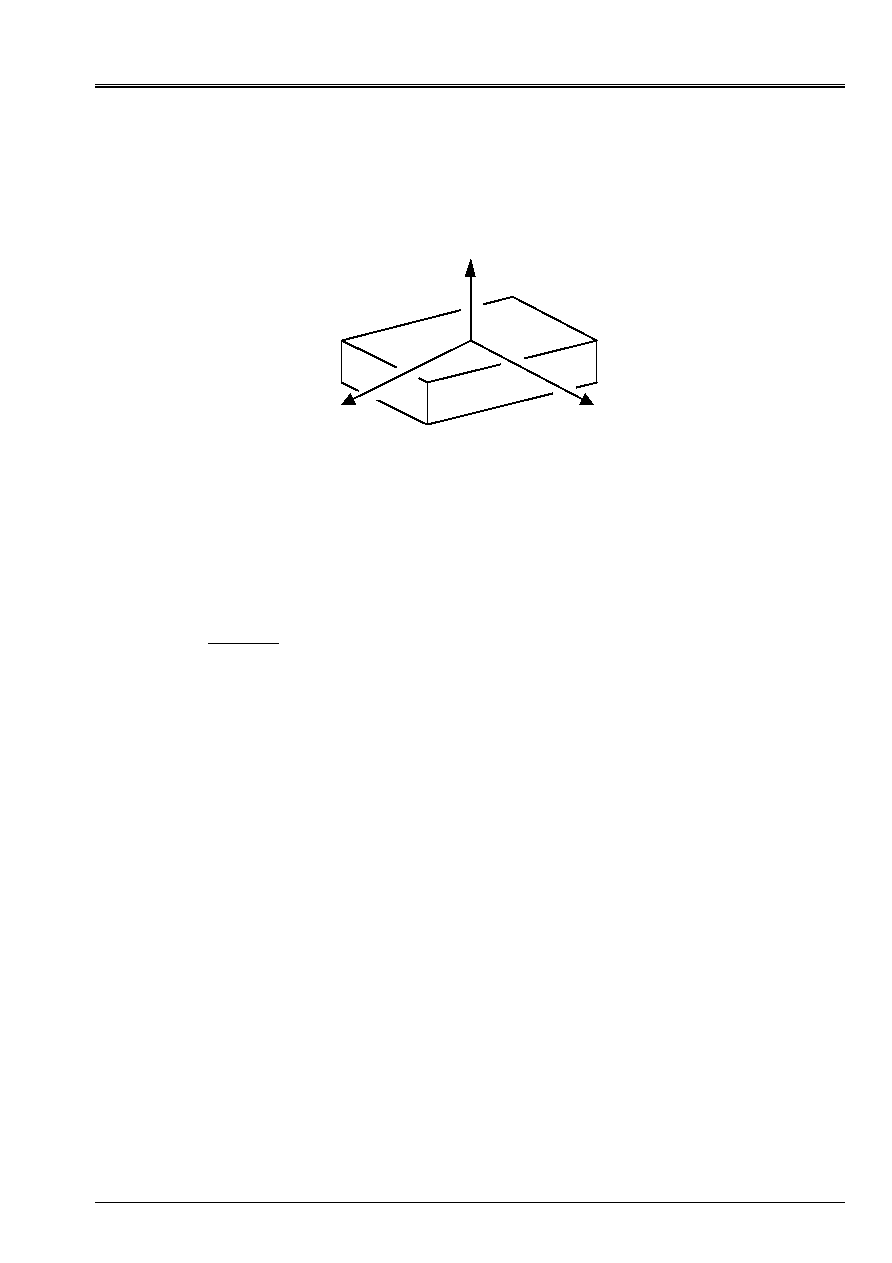
To define the reference mark of orthotropism (L, T, NR) related to the elements, one can refer to documentations
[U4.42.03]
DEFI_COQU_MULT
and [U4.42.01]
AFFE_CARA_ELEM
.
NR
T
L
L, T and NR: directions of orthotropism
longitudinal, transverse and normal
/ELAS_ORTH = _F
(
E_L = ygl
Longitudinal Young modulus.
E_T = ygt
Transverse Young modulus.
E_N = ygn
Normal Young modulus.
GL_T = glt
Modulus of rigidity in plan LT.
G_TN = gtn
Modulus of rigidity in plan TN.
G_LN = gln
Modulus of rigidity in plan LN.
NU_LT = nult
Poisson's ratio in plan LT.
NU_TN = nutn
Poisson's ratio in plan TN.
NU_LN = nuln
Poisson's ratio in plan LN.
Important remark:
The talk of this note of reference is based on the convention of the books of J.L.Batoz and D. Gay.
Documentation U of DEFI_MATERIAU describes these choices, and coefficient NU_LT is interpreted
the following way in Aster:
if one exerts a traction according to the axis
L
giving place to a deformation according to this axis equalizes with
ygl
L
L
=
, there is a deformation according to the axis
T
equalize with:
ygl
*
- nult
L
T
=
.

Code_Aster
®
Version
6.4
Titrate:
Anisotropic elasticity
Date
:
28/10/03
Author (S):
A. ASSIRE
Key
:
R4.01.02-A
Page
:
14/14
Manual of Reference
R4.01 booklet: Composite materials
HT-66/03/005/A
5 Bibliography
[1]
J.C. MASSON: Stamp of Hooke for orthotropic materials, internal Rapport
Applications in Mechanics, n°79-018, CiSi, 1979.
[2]
D. GAY: Composite materials, Hermes Edition, 1987
[3]
J.L. BATOZ, G. DHATT: Modeling of stuctures by finite elements, Volume 1, Edition
Hermes