|
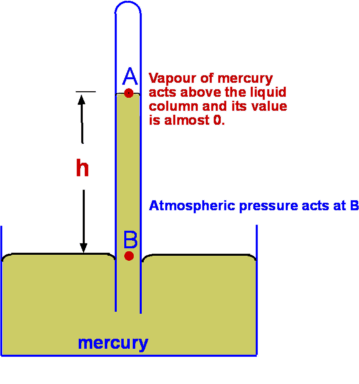
| Figure 2.9 : Mercury Barometer |
Mercury Barometer (Fig.2.9) is the simplest device to
measure atmospheric pressure at a location. It consists of a glass
tube closed at one end immersed in a container filled with
mercury. Because of the atmospheric pressure mercury rises in the
tube as shown. If 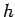 is the height of mercury above the fluid
level in the container, we have is the height of mercury above the fluid
level in the container, we have
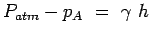 |
(2.27) |
where 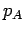 is the pressure at A and will be equal to the vapour
pressure of mercury, is the pressure at A and will be equal to the vapour
pressure of mercury, 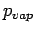 , which is around 0.16pa at a
temperature of , which is around 0.16pa at a
temperature of 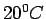 . It is usual to neglect . It is usual to neglect 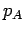 when the
atmospheric pressure is given as when the
atmospheric pressure is given as
Sometimes atmospheric pressure is expressed as "mms of mercury"
being equal to 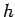 . At sealevel conditions where the pressure
value is 101,327 Pascals and the specific weight of mercury is
133,100 N/m3, the barometric height is 761 mm Hg. Water could
be used as the barometer fluid, but in that case the height of
water will be around 10.36m! . At sealevel conditions where the pressure
value is 101,327 Pascals and the specific weight of mercury is
133,100 N/m3, the barometric height is 761 mm Hg. Water could
be used as the barometer fluid, but in that case the height of
water will be around 10.36m!
(c) Aerospace, Mechanical & Mechatronic Engg. 2005
University of Sydney
| 
