Microprocessor and Memory Basics
Abstract system architecture
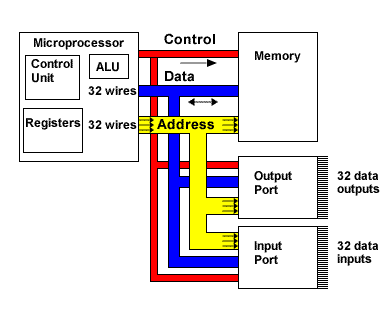
A typical system architecture for a computer will have three principal blocks:
- The Microprocessor itself consisting of:
- an Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU) that performs mathematical and logical computations;
- a Control Unit that manages the execution of instructions;
- and multiple Registers that are used as temporary storage for instructions and data.
- Memory, which is used to store both the instructions to be executed by the microprocessor and the data to be used in the computation.
- Input and Output ports which interface the processor to the external world, including keyboards, mice, monitors, hard disc drives, etc.
Processor Schematic Architecture